This article documents how to get the traceback information of all threads / concurrent threads in a multi-threaded, multi-coordinated (gevent), asyncio program.
Get traceback information for all threads¶
You can get information about all threads by using threading.enumerate(), Get the thread traceback information via sys._current_frames().
Test program:
import sys
import traceback
import threading
import time
def do(x):
x = x * 3
time.sleep(x * 60)
def main():
threads = []
for x in range(3):
t = threading.Thread(target=do, args=(x,), name='thread-{}'.format(x))
t.start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
id2thread = {}
for thread in threading.enumerate():
id2thread[thread.ident] = thread
for thread_id, stack in sys._current_frames().items():
stack_list = traceback.format_list(traceback.extract_stack(stack))
print('thread {}:'.format(id2thread[thread_id]))
print(''.join(stack_list))
Result:
$ python test.py
thread <Thread(thread-2, started 123145466843136)>:
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/threading.py", line 884, in _bootstrap
self._bootstrap_inner()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/threading.py", line 916, in _bootstrap_inner
self.run()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/threading.py", line 864, in run
self._target(*self._args, **self._kwargs)
File "test.py", line 9, in do
time.sleep(x * 60)
thread <Thread(thread-1, started 123145461587968)>:
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/threading.py", line 884, in _bootstrap
self._bootstrap_inner()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/threading.py", line 916, in _bootstrap_inner
self.run()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/threading.py", line 864, in run
self._target(*self._args, **self._kwargs)
File "test.py", line 9, in do
time.sleep(x * 60)
thread <_MainThread(MainThread, started 140736955184064)>:
File "test.py", line 27, in <module>
stack_list = traceback.format_list(traceback.extract_stack(stack))
Get the traceback information for all gevent processes¶
You can get all the objects with gc.get_objects() and filter out all the concurrent objects from them (greenlet.greenlet), The traceback information is then obtained from the gr_frame property of the greenlet object.
Example:
import gc
import traceback
import gevent
import greenlet
def foo():
while True:
for x in range(10):
gevent.sleep(x * 10)
def bar():
while True:
for x in range(5):
gevent.sleep(x * 20)
def main():
for func in [foo, bar]:
t = gevent.spawn(func)
t.start()
def get_traceback():
for obj in gc.get_objects():
if isinstance(obj, greenlet.greenlet):
stack_list = traceback.format_list(
traceback.extract_stack(obj.gr_frame)
)
print('greenlet {}:'.format(obj))
print(''.join(stack_list))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
gevent.spawn(get_traceback).join()
Result:
$ python test.py
greenlet <Greenlet at 0x103f4ca60: bar>:
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/greenlet.py", line 536, in run
result = self._run(*self.args, **self.kwargs)
File "test.py", line 17, in bar
gevent.sleep(x * 20)
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/hub.py", line 167, in sleep
waiter.get()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/hub.py", line 898, in get
return self.hub.switch()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/hub.py", line 630, in switch
return RawGreenlet.switch(self)
greenlet <Greenlet at 0x103f4caf8: get_traceback>:
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/greenlet.py", line 536, in run
result = self._run(*self.args, **self.kwargs)
File "test.py", line 30, in get_traceback
traceback.extract_stack(obj.gr_frame)
greenlet <greenlet.greenlet object at 0x103f4c0e0>:
File "test.py", line 38, in <module>
gevent.spawn(get_traceback).join()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/greenlet.py", line 496, in join
result = self.parent.switch()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/hub.py", line 630, in switch
return RawGreenlet.switch(self)
greenlet <Greenlet at 0x103f4c930: foo>:
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/greenlet.py", line 536, in run
result = self._run(*self.args, **self.kwargs)
File "test.py", line 11, in foo
gevent.sleep(x * 10)
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/hub.py", line 167, in sleep
waiter.get()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/hub.py", line 898, in get
return self.hub.switch()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/hub.py", line 630, in switch
return RawGreenlet.switch(self)
greenlet <Hub at 0x103f4c9c8 select default pending=0 ref=2>:
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/site-packages/gevent/hub.py", line 688, in run
loop.run()
Get the traceback information for all asyncio tasks¶
You can get all asyncio task objects with asyncio.Task.all_tasks(), then get the traceback information from the get_stack() method of the task object.
Example:
import asyncio
import traceback
async def foo():
while True:
for x in range(10):
print('foo')
await asyncio.sleep(x * 10)
async def bar():
while True:
for x in range(5):
print('bar')
await asyncio.sleep(x * 20)
async def get_traceback(loop):
await asyncio.sleep(1)
for task in asyncio.Task.all_tasks(loop):
stack_list = []
for stack in task.get_stack():
stack_list.extend(
traceback.format_list(traceback.extract_stack(stack))
)
print('asyncio task {}:'.format(task))
print(''.join(stack_list))
if __name__ == '__main__':
event_loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
try:
tasks = [foo(), bar(), get_traceback(event_loop)]
event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
finally:
event_loop.close()
Result:
bar
foo
bar
foo
asyncio task <Task pending coro=<wait() running at /xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/tasks.py:307> wait_for=<Future pending cb=[<TaskWakeupMethWrapper object at 0x10c57c258>()]> cb=[_run_until_complete_cb() at /xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py:176]>:
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/tasks.py", line 307, in wait
return (yield from _wait(fs, timeout, return_when, loop))
asyncio task <Task pending coro=<bar() running at test.py:16> wait_for=<Future pending cb=[<TaskWakeupMethWrapper object at 0x10c57c378>()]> cb=[_wait.<locals>._on_completion() at /xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/tasks.py:374]>:
File "test.py", line 16, in bar
await asyncio.sleep(x * 20)
asyncio task <Task pending coro=<get_traceback() running at test.py:27> cb=[_wait.<locals>._on_completion() at /xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/tasks.py:374]>:
File "test.py", line 35, in <module>
event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
File "test.py", line 35, in <module>
event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 454, in run_until_complete
self.run_forever()
File "test.py", line 35, in <module>
event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 454, in run_until_complete
self.run_forever()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 421, in run_forever
self._run_once()
File "test.py", line 35, in <module>
event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 454, in run_until_complete
self.run_forever()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 421, in run_forever
self._run_once()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 1425, in _run_once
handle._run()
File "test.py", line 35, in <module>
event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 454, in run_until_complete
self.run_forever()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 421, in run_forever
self._run_once()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 1425, in _run_once
handle._run()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/events.py", line 126, in _run
self._callback(*self._args)
File "test.py", line 35, in <module>
event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 454, in run_until_complete
self.run_forever()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 421, in run_forever
self._run_once()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/base_events.py", line 1425, in _run_once
handle._run()
File "/xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/events.py", line 126, in _run
self._callback(*self._args)
File "test.py", line 25, in get_traceback
traceback.format_list(traceback.extract_stack(stack))
asyncio task <Task pending coro=<foo() running at test.py:9> wait_for=<Future pending cb=[<TaskWakeupMethWrapper object at 0x10c57c3d8>()]> cb=[_wait.<locals>._on_completion() at /xxx/lib/python3.6/asyncio/tasks.py:374]>:
File "test.py", line 9, in foo
await asyncio.sleep(x * 10)
What is the use of knowing how to get traceback information? traceback information is very useful for debugging our programs, especially for debugging running processes.
If you feel that the traceback information is a little short, you can process the traceback: Use raven to expand the traceback information and send it to sentry.
Using raven to expand and collect traceback information¶
The source code and local variables in the traceback information can be retrieved through raven, which is very helpful to diagnose the problem quickly. We can also send the information to sentry for archiving and visualizing the traceback information.
Example:
import sys
import threading
import time
import traceback
from raven import Client
from raven.utils.stacks import get_stack_info
def foo(n):
while True:
for x in range(n):
print('foo')
time.sleep(x * 0.5)
def bar():
foo(233)
def main():
t = threading.Thread(target=bar, name='bar')
return t
def get_traceback(raven_client):
id2thread = {}
for thread in threading.enumerate():
id2thread[thread.ident] = thread
for thread_id, stack in sys._current_frames().items():
frames = traceback.walk_stack(stack)
stacktrace = get_stack_info(frames)
thread = id2thread[thread_id]
print('thread: {}'.format(thread))
print(raven_client.captureMessage(
'traceback from {}'.format(thread),
stack=True,
data={
'stacktrace': stacktrace,
},
extra={
'thread': thread,
}
))
if __name__ == '__main__':
raven_client = Client()
t = main()
t.start()
time.sleep(1)
get_traceback(raven_client)
t.join()
Result:
$ python test2.py foo foo foo thread: <Thread(bar, started 123145482194944)> e800cefdc2ce4a00bb716b8342c75a96 thread: <_MainThread(MainThread, started 140736955184064)> 86b0cb00d5884cb49ba033d83e21040f foo foo
Info on sentry :
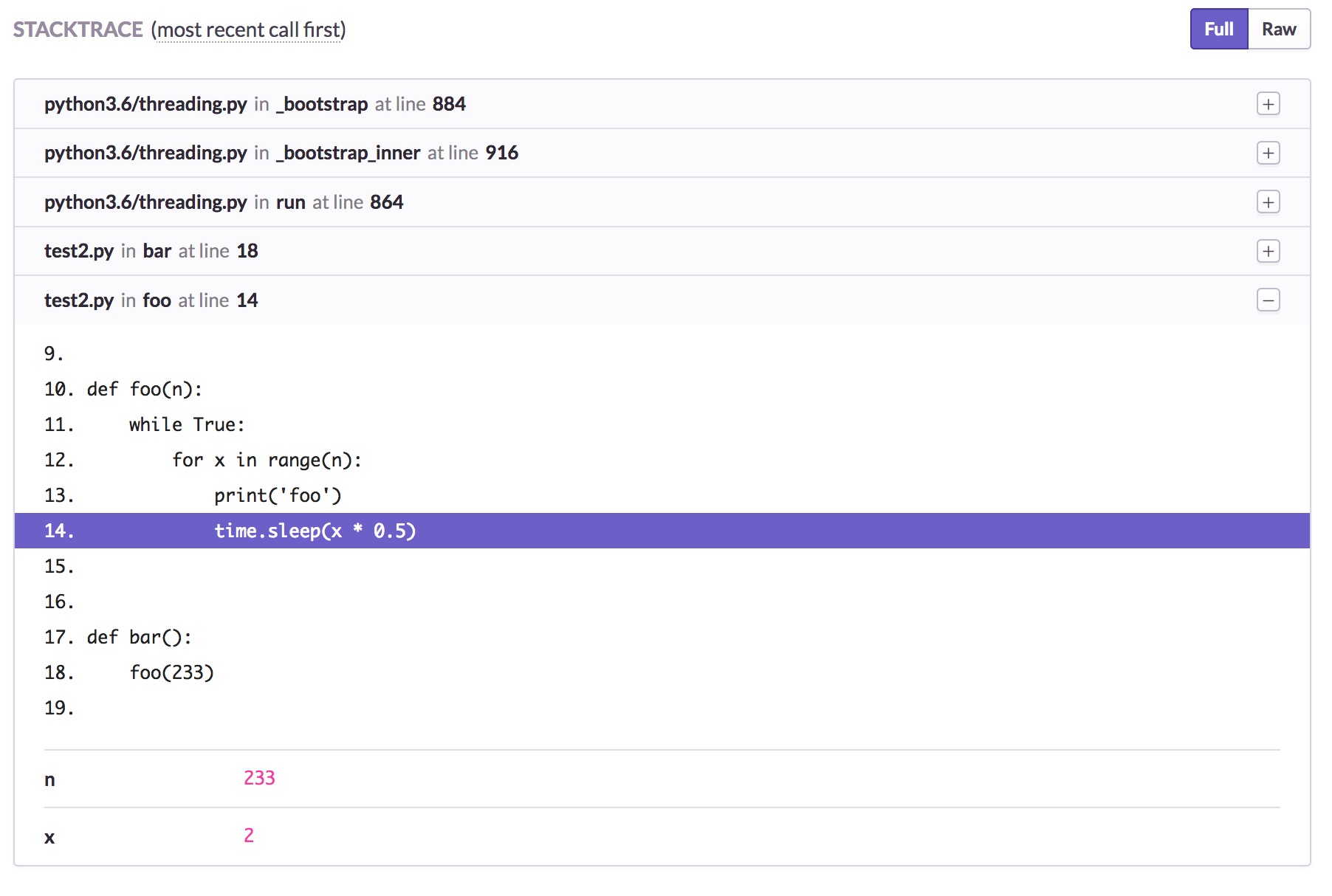
References¶
- 17.1. threading — Thread-based parallelism — Python 3.6.4rc1 documentation
- 29.1. sys — System-specific parameters and functions — Python 3.6.4rc1 documentation
- 29.9. traceback — Print or retrieve a stack traceback — Python 3.6.4rc1 documentation
- greenlet: Lightweight concurrent programming — greenlet 0.4.0 documentation
- 29.11. gc — Garbage Collector interface — Python 3.6.4rc1 documentation
- 18.5.3. Tasks and coroutines — Python 3.6.4rc1 documentation
- getsentry/raven-python: Raven is a Python client for Sentry (getsentry.com)
Comments