题目¶
原题地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/n-ary-tree-preorder-traversal/
Given an n-ary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Follow up:
Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Example 1:
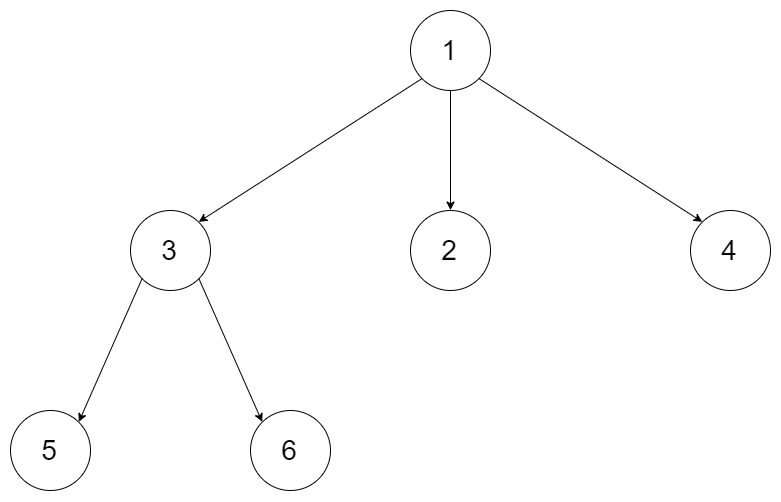
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: [1,3,5,6,2,4]
Example 2:
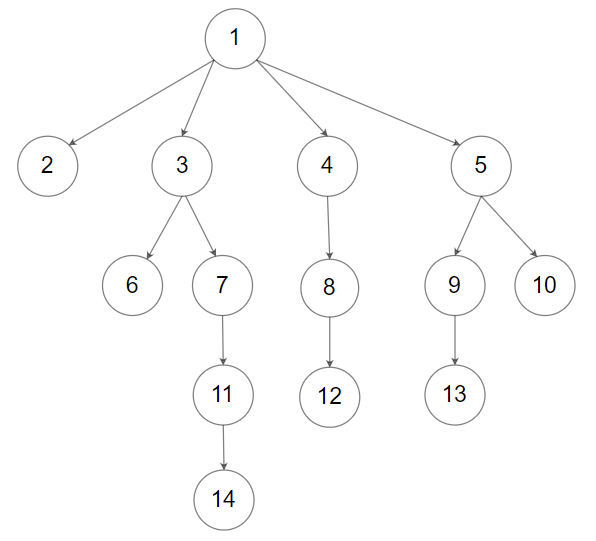
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] Output: [1,2,3,6,7,11,14,4,8,12,5,9,13,10]
Constraints:
- The height of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to 1000
- The total number of nodes is between [0, 10^4]
解法¶
这个题目虽然说的是 N 叉树的前序遍历,但是实现方法跟二叉树的前序遍历几乎是一样的, 可以参考前面 LeetCode: 144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal 的方法进行实现。
递归法实现¶
这个方法的 Python 代码类似下面这样:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def preorder(self, root):
nodes = []
self._preorder(root, nodes)
return nodes
def _preorder(self, root, nodes):
if root is None:
return
nodes.append(root.val)
for c in root.children:
self._preorder(c, nodes)
stack 法实现¶
这个方法的 Python 代码类似下面这样:
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val=None, children=None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def preorder(self, root):
if root is None:
return []
nodes = []
stack = []
stack.append(root)
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
nodes.append(node.val)
# 因为 stack 是后进先出,所以要反着来
for c in node.children[::-1]:
stack.append(c)
return nodes
Comments